Session 3: Side Wind Condition
Objective1: To give essential concepts of management of side wind condition during take off and landing phases
Objective2: To give ideas of critical potential critical problem of the above condition
Explanation:
The teaching materials will utilized to give some examples of management and critical problem of side wind condition in take off and landing phases
Material:
- Multimedia black board + Power Point Like Software
- Photos / Videos
- Pictures
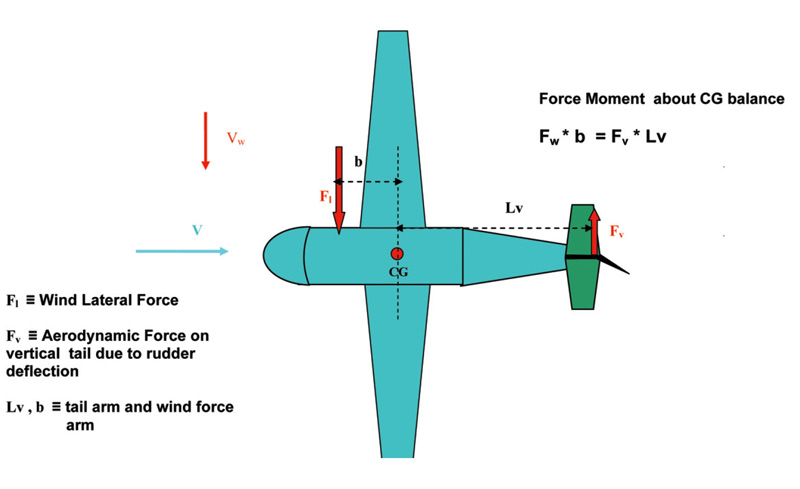
Figure 13 Side wind condition
Main activities
- By pictures and (if possible) by videos will be explain the management and the critical problems in the event of side wind in take off and landing phases.
- Student will be asked to think about extreme situation for this event
Maximum duration:
30 minutes
Main question to be asked:
- What is the most important airplane part concerning the capability of side wind control?
- What is the above event more critical for each airplane configuration?
Developing of Activity
- Make the students understand how is managed a wind side condition at takeoff and landing phases
- Make the students to figure out critical situations in side wind conditions in take off /landing phases
Results of Activity
- The force and force moment (about the Centre of Gravity) of the aerodynamic force due to wind side effect is balanced by the aerodynamic lateral force on the vertical tail due to rudder deflection.
- It is mandatory that the airplane maintain the runway direction during the take off or the landing phases.
Experiment: A Kid Balloon
Description
Take a kid balloon. Blow up it until the explosion.
Explanation
By blowing up a kid balloon you increase the air mass inside the balloon. For the gases lows the(thermodynamic) inside increase its values, it overcomes the external atmospheric (static) pressure, so the balloon tends to inflate. The thin container balance the differential pressure by its internal capability to withstand traction loads. When the limit traction load of the thin container is reached the balloon explodes.
Figure 19 Kid Balloon
Results
A pressurized fuselage of an airplane flying at high altitude is subjected to a differential pressure between the external atmosphere pressure (at 10000 m is about 1/3 than at sea level) and the internal pressure (equivalent to that at 2000 m altitude). The resultant force due to this differential pressure is balanced by the fuselage skin to withstand traction loads.
So a pressurized fuselage has to be designed to withstand the differential pressure effect besides many others loads.
